Electrical Safety Work Process
02.01.2022
CONTENTS:
- What is an electrically safe working procedure?
- What is the first safety step when working on electrical systems?
- Electrical Safety Work Practices Plan
- Identify Power Sources
- Disconnect Power Sources
- Lockout/Tagout
- Discharge Stored Electrical Energy
- How to eliminate electrical overloads
Electrical shock hazards are something that should be taken seriously in the workplace. Every organization should conduct an electrical safety program for all of its employees. In addition to informing them of the hazards, employees should also take a safety seminar.
The main causes of overloading are:
- Inadequate conductor cross-section to the operating current (e.g., when wiring to a bell is done with telephone wire).
- Parallel connection of unrated current collectors into the network without increasing the cross-sectional area of the conductors (for example, an extension cord with 3 or 4 sockets into one working socket).
- Leakage currents and lightning striking conductors.
- Increased ambient temperature.
In addition, when the power grid is overloaded, the devices and appliances connected to it, constantly experience a shortage of current, which can lead to their emergency failure
What is an electrically safe working procedure?
The electrically safe work condition must be ensured by:
- Maintaining appropriate distances to live parts or by covering, enclosing live parts;
- Use of device interlocks and barriers to prevent erroneous operations and access to live parts;
- Use of warning alarms, signs, and placards;
- Use of devices to reduce the intensity of electric and magnetic fields to permissible values;
- Use of protective equipment and devices, including protection against electric and magnetic fields in electrical installations, where their intensity exceeds permissible standards.
What is the first safety step when working on electrical systems?
Many workers in the workplace do not pay much attention to electrical hazards. Some believe that electrical incidents are a part of life, and some even believe that they will never have an accident. Worst of all, some employees believe that health risks are part of their jobs and cannot be avoided. This type of careless attitude among employees leads to more work-related injuries. To make an effective change in an employee's perspective, a safety program is paramount.
Electrical safety courses should be taken:
- Company managers, specialists responsible for organizing work closely related to electricity;
- Full-time employees whose activities are related to working on electrical installations of various types and capacities;
- Occupational safety specialists, who inspect electrical equipment and monitor compliance with regulations during the organization and execution of work.
Electrical equipment safety is provided for organizations that use electricity for their needs as well as for electricity suppliers.
Electrical Safety Work Practices Plan
Let's now look at a few precautions: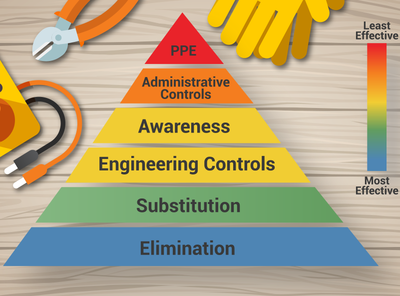
- Make a safety plan that includes emergency actions, evacuations that meet codes and standards.
- Professional and trained electricians should be hired who understand safety practices in electricity and the workplace environment.
- Workers must use non-conductive gloves, safety glasses, shoes, and protective clothing to protect against electric shock.
- Maintenance and testing should be performed periodically.
- Make a safety plan that includes emergency actions, evacuations that comply with codes and standards.
- Professional and trained electricians should be hired who understand safety rules and the workplace environment.
- Workers must use non-conductive gloves, safety glasses, shoes, and protective clothing to protect against electric shock.
Maintenance and testing should be performed periodically and regularly.
Identify Power Sources
The power supply is a device directly connected to the primary network 220/380 V/50 Hz, so the electrical safety of the entire final product will depend on its circuitry and design, and it must necessarily be ensured by the appropriate class. Requirements for electrical safety of power supplies are derived from the requirements for electrical safety of luminaires, which can be found in the appendix.
According to the mentioned normative document, luminaires are divided into three classes according to the type of protection against electric shock. In luminaires made by the electrical safety class, protection against electric shock is provided by basic insulation and additional protective earthing. In this case, the luminaire insulation is tested with a test voltage of 1.44 kV, and the luminaire is connected to the network with a three-wire cable.
In luminaires made according to electrical safety class II, protection against electric shock is provided by basic and additional or reinforced insulation. In this case, the test voltage is 3.6 kV and the luminaire is allowed to be connected to the network with a two-wire cable.
In luminaires of electrical safety class III (the safest luminaires), protection against electric shocks is provided by using a safety extra-low voltage (SELV), which must not exceed 50V AC or 120V DC and must be isolated from the primary network if a surge converter is used as the source of the SELV. The test voltage for this class of luminaire is 0.5kV.
On the basis of what class of electrical safety the luminaire is designed for, when selecting a power supply you should pay attention to such its parameter as the electrical strength of isolation "input-output" and/or "input-housing" and, applying some or other design solutions, not to worsen in the final product the value of this parameter.
Disconnect Power Sources
In case of emergency or abnormal situations, the employee is obliged to disconnect the electrical equipment from the mains, and if it is not possible to do so, to take measures to prevent people from getting into the danger zone. Inform your supervisor, another responsible person, or the company's electrical staff about electrical equipment malfunctions. The lighting may be switched off at the same time as a result of a disconnected electrical device. If there is no natural light, use an emergency light or a hand-held light (cell phone, battery-powered lantern).
Lockout/Tagout
The Lockout/Tagout system is a planned safety technique that provides for disconnecting the power supply to industrial equipment and appliances during maintenance or repair work. This procedure helps protect workers from risks associated with energized or energized equipment.
Why this system is needed:
- To ensure the safe performance of maintenance, cleaning, and repair work.
- Prevent injury.
- Preventing damage to equipment.
- Help prevent errors from occurring.
- It is a procedure that provides a clear warning of a hazard in the workplace.
Discharge Stored Electrical Energy
All electrical safety rooms fall into several categories:
- High Hazard. These are rooms where there are conditions that contribute to an increased risk of electric shock: high humidity, dust, conductive coatings, high temperatures, presence of opportunities to touch metal structures and electrical equipment at the same time.
- Particularly hazardous areas. These are rooms that must combine at least two components of the previous point at the same time. Buildings of this type also include those with, particularly damp conditions. Another factor contributing to this category is an active chemical environment.
- No high hazard. These are structures that do not have the conditions listed in the previous paragraphs.
How to eliminate electrical overloads
Be that as it may, if your circuit breakers periodically "go out", and it happens sometime after you turn on the appliances, then there is a very big problem of overloading in the network.
There are several solutions to this problem:
- If the cable cross-section allows, increase the rating of the circuit breaker;
- If the cross-section of cable or wires is minimal, such as the old aluminum, then separate the sockets in this group and spend an additional group of outlets from the apartment panel or floor panel.
- If you have an old automatic circuit breaker, it is possible that false tripping due to the age of the circuit breaker. Remove the old circuit breaker and install a new circuit breaker, this may help.
- Lastly, don't use tees and minimize the use of extension cords. A large number of outlets provokes the inclusion of additional appliances and can lead to overloading.
Important! Frequent tripping of circuit breakers, a real consequence of overloading. Overloading should be taken seriously. Overloading is the heating of the wiring, and where there is heat, it is not far from a fire.