Encoder Interface Types
02.05.2023
Encoders are position sensors that are used in industrial electric drives to obtain information about the speed of rotation of the electric motor and the position of the rotor shaft. With the help of an encoder, feedback on the speed or position of the electric machine is implemented, which is brought into the automatic control system and used in the machine control algorithm. This connection is the backbone of the automated electric drive system.
Many different communication interfaces have been developed for encoders over the past years. But the choice of communication interface puts before the developer several factors - cost-effectiveness, accuracy, and security. Let's find out what types of encoder interface exist.
What Is the Interface of the Encoder?
Encoder interfaces are devices that are specifically designed to read encoder pulses and convert them into encoder position, Also they are needed to process other data, send information to the encoder PLC interface and make it available to external circuitry.
Parallel Encoder Interface
The classic approach to encoder wiring is to connect the encoder in parallel. This scheme requires at least one twisted pair per bit (high data level and low data level) as well as VCC and ground. The advantage is that all bits are transmitted simultaneously, which minimizes latency. The disadvantage is that increasing the number of wires increases cost, complexity, the potential for error, and additional points of failure.
Serial Encoder Interface
Serial interfaces provide a simpler, faster, and more reliable way to transfer data from the encoder to the controller/counter. A key advantage over traditional parallel circuits is that they combine data to minimize the number of connections. Instead of requiring one twisted pair (high-level data, low-level data) per bit, a serial interface uses one twisted pair to serialize data from all bits, reducing the number of wires compared to parallel output.
A serial interface connects one slave device to one master device. Thus, it is considered a point-to-point connection scheme. In a point-to-point connection scheme, the clock remains high until the master needs information from the encoder. When the master interrogates the encoder, the encoder returns a clock stream equivalent to the information received from the encoder.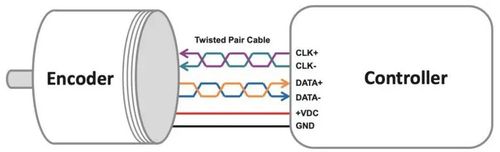
Several different serial interfaces have been installed. Some of them, such as serial synchronous interface (SSI interface encoder) and bi-directional synchronous serial interface (BiSS), are open source, while others are proprietary.
- SSI encoder. SSI is a widely used point-to-point serial interface between a PLC/host and an encoder. It is based on the RS422 standard.
- BiSS encoder. The BiSS (bidirectional/serial/synchronous) interface protocol is an open-source digital interface that provides digital, serial, and secure communication between the controller, encoder, and actuator.
- BiSS Line. It uses basic BiSS definitions and device content but displays communication over a half-duplex RS485 line. The BiSS Line protocol can be used with either a 2-wire or 4-wire setup. The 2-wire setup combines communication and power over a single twisted pair of lines. BiSS Line supports the multi-device operation and preemptive error correction (FEC).
The BiSS interface protocol (bi-directional/serial/synchronous) is an open-source digital interface that provides digital, serial, and secure communication between the controller, sensor, and actuator.
Fieldbus Encoder Interface
Fieldbus protocols remove the limitations of point-to-point protocols by allowing a single controller to communicate with many analog and digital devices simultaneously. Connecting to any device on the network allows the user to communicate with all devices on the network.
Profibus encoder
Profibus is available on many PLCs and is one of the most common Fieldbus technologies in factory automation and other fields. It is based on RS485.
DeviceNet
DeviceNet is a Fieldbus system based on CAN networks and the CIP protocol. DeviceNet is controlled by ODVA, is widely used in factory automation, and is available on many PLCs.
Interbus
Developed by Phoenix Contact in the mid-1980s, Interbus is the oldest open industrial network. Interbus is divided into two buses. The remote bus is an RS-485 transmission medium with a length of up to 13 km. The local or peripheral bus allows up to eight Interbus encoders to be connected over a distance of up to 10 m.
CANOpen
CANopen is a Fieldbus protocol that uses CAN networks. CANopen is available on many PLCs and is widely used in factory automation and mobile machines.
CANOpen Safety
The CANopen Safety platform for safety-related communication is a complement to the CANopen application layer and the communication profile.
CANopen Lift
CANopen Lift is a Fieldbus protocol for elevator applications. It is similar to CANopen and is based on the use of CAN networks.
Ethernet Encoder Interface
Ethernet is becoming an increasingly popular networking approach for industrial automation. Ethernet allows multiple devices to connect to networks with different topologies. As with a Fieldbus, the connection to any device on the network allows the user to access and control any device on the network.
The main difference between conventional Fieldbuses and Ethernet networks is that Fieldbus protocols are deterministic, based on "best effort" delivery. When data conflicts occur, which is possible on this type of network, one transmission will be delayed.
In response to this problem, several different industrial Ethernet standards have been developed. Some require ASICS in hardware, while others are based solely on software. When deciding, it is important to remember that for many applications, the latency level provided even without special conditions is good enough to serve even fast applications.
Modbus
Modbus is a serial protocol controlled by the Modbus organization.
EtherCAT
The EtherCAT encoder protocol is optimized for cyclic process data with the integration of a chip in each slave device instead of the TCP/IP stack as in Ethernet. EtherCAT encoders have short cycle times and are ideal for high-speed and position control applications that require real-time data with deterministic response times.
Profinet encoder
The next evolution of Profibus, Profinet has become one of the leading Ethernet-based protocols on the market. Profinet allows the addition and replacement of devices or modules on the fly without stopping the whole machine and is ideal for creating very flexible modular machines.
EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP is an industrial communication protocol developed by Rockwell Automation and managed by ODVA. It is based on CIP and TCP/IP.
Ethernet Powerlink
Ethernet Powerlink is a real-time communication system based on Ethernet networks and controlled by EPSG.
What Is Absolute Encoder Interface
The incremental encoder output is a stream of pulses on one or more channels, and the absolute encoder output is a multi-bit word. Encoder interface protocols provide a common language for the encoder and control system to interpret the absolute encoder's multi-bit word output for information including discrete position, speed, and more.  Common encoder interface protocols for absolute encoders include:
Common encoder interface protocols for absolute encoders include:
- parallel,
- serial,
- Fieldbus, and
- Ethernet options.