Laser distance sensors overview
28.06.2024
Laser distance sensors are revolutionizing industrial automation with their precision and reliability. These sensors are crucial for many applications, including robotics and manufacturing, as they use laser technology to detect distances. Their exceptional precision makes it possible to increase industrial operations' productivity and efficiency. The various kinds of laser distance sensors, their operation, and useful installation and maintenance advice will all be covered. You can choose the best sensor for your application and guarantee peak performance from your automation systems by being aware of these factors.
What are Laser Distance Sensors?

The distance between a target object and the sensor is determined using precise instruments known as laser distance sensors. They work by directing a laser beam in the direction of the target and timing the return of the reflected beam. The Time-of-Flight (ToF) principle is the method that makes it possible to measure distances with extreme accuracy.
Importance in Industrial Automation
Distance-detecting lasers are very valuable in the field of industrial automation because of their accuracy, adaptability, and effectiveness. Here are some key reasons why they are so important:
1. High Precision and Accuracy
Laser distance sensors provide extremely accurate measurements, which is crucial for applications requiring fine tolerances. This precision helps improve the quality of products and processes in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and electronics.
2. Non-Contact Measurement
The ability of laser distance sensors to measure without making touch is one of its main features. When it is not feasible to make physical touch with the target or when doing so could harm the object or sensor, this capability is especially helpful.
3. Fast Response Time
Industrial automation often requires real-time measurements to control and adjust processes on the fly. Quick reaction times are provided by laser distance sensors, enabling quick feedback and adjustments. This capability is essential in applications like robotic guidance, where timely data is critical for precise movement and positioning.
4. Versatility
Laser distance sensors are extremely adaptable and have a wide range of uses in various sectors. From measuring the dimensions of parts on an assembly line to monitoring the position of objects in warehouses, their adaptability makes them a valuable tool in industrial automation.
5. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
Laser distance sensors facilitate process optimization and error reduction by offering precise and dependable measurements. This improvement leads to higher efficiency and productivity, ultimately resulting in cost savings for businesses.
6. Robustness and Durability
Industrial environments can be harsh, with conditions such as dust, moisture, and temperature extremes. Laser distance sensors are designed to withstand these challenges, offering robust performance and durability. Their resilience makes them suitable for use in demanding applications, ensuring consistent operation even in adverse conditions.
7. Integration with Automation Systems
It is simple to combine laser distance sensors with a variety of automation systems, including Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). This seamless integration enables better control and monitoring of automated processes, enhancing overall system efficiency.
8. Safety and Quality Control
Laser distance sensors are quite important in businesses where quality control and safety are top priorities. By ensuring that items adhere to predetermined measurements and tolerances, they lower the possibility of errors and raise overall quality. Moreover, laser sensors increase safety in applications like automated vehicle guidance by providing collision avoidance systems with accurate distance readings.
Laser sensor working principle
Utilizing the unique characteristics of laser light, laser distance sensors are intriguing gadgets that provide extremely accurate distance measurements.
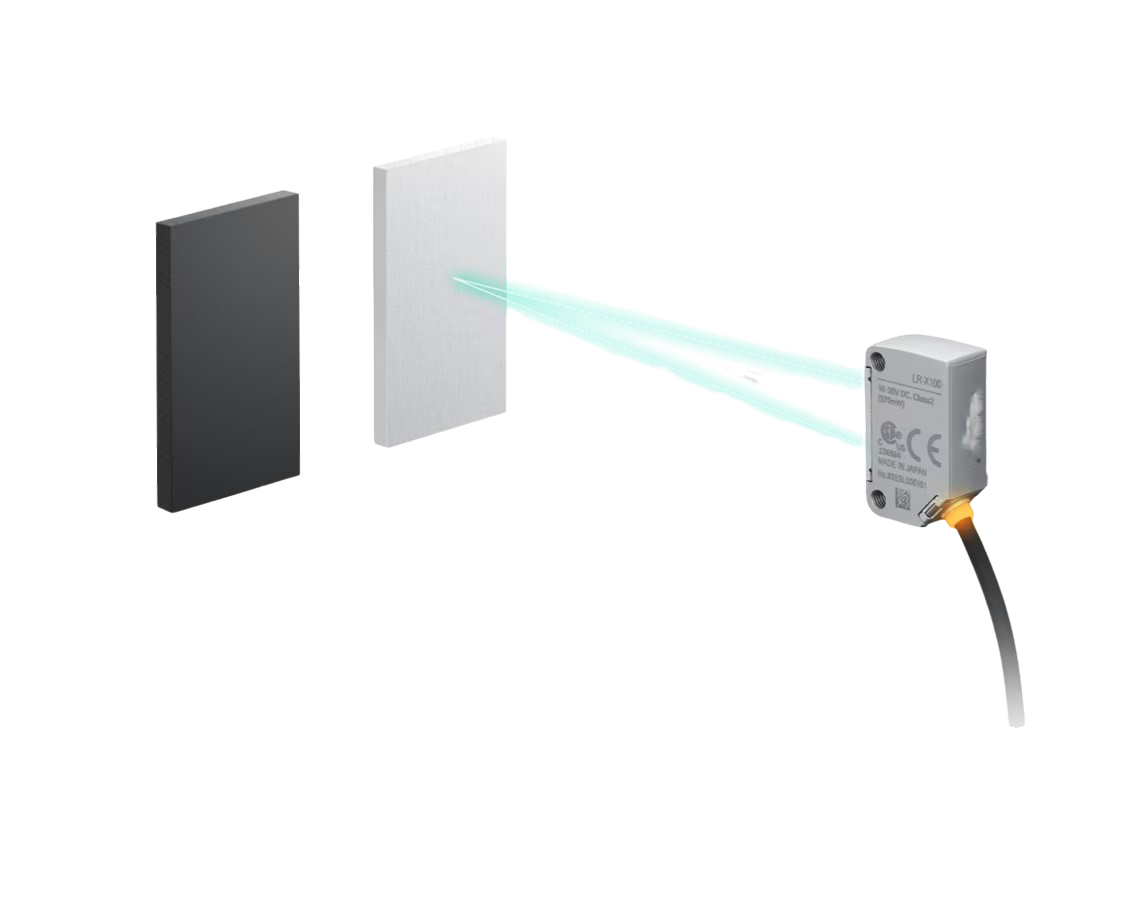
Basic mechanics
- A laser sensor consists of three main components: a laser source, an optical system, and a photodetector.
- The laser source emits a thin beam of light.
- This beam of light is focused by the optical system.
- The reflected light is received by the photodetector.
- Light is converted into an electrical signal by the photodetector.
Triangulation is the basis for how laser sensors function. This means that they measure the distance to an object by calculating the angle between the laser source, the object, and the photodetector. The larger the angle, the closer the object is.
Light emission and reflection
- Visible or invisible laser radiation is used by laser sensors.
- The wavelength of the laser radiation determines how it interacts with the object.
- Some objects absorb laser light, while others reflect it.
- The angle at which the laser radiation is reflected depends on the properties of the object.
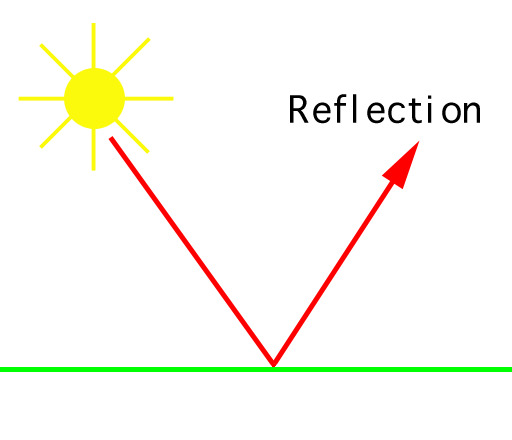
The properties of the object being measured affect how it interacts with the laser radiation. For example, matte surfaces reflect more light than shiny surfaces. The color of an object can also affect how it reflects laser radiation.
Calculate the distance
- The distance to an object can be calculated using trigonometry.
- The angle between the laser source, the object, and the photodetector is known.
- The distance between the laser source and the photodetector is also known.
- This information can be used to calculate the distance to the object.
The formula for calculating the distance to an object is as follows:
d = (L * sin(θ)) / sin(180° - θ)
where:
d - distance to the object
L is the distance between the laser source and the photodetector
θ - the angle between the laser source, the object and the photodetector
Laser sensors are accurate and dependable tools for location, speed, and distance measurements. They are an important resource for numerous sectors.
Types of laser sensors
There are many different kinds of laser distance sensors, and each is made to fulfill particular application needs and provide special benefits. Choosing the appropriate laser sensor for a given task can be made easier by being aware of the various laser sensor types.
Discrete output sensors
- When an object is present, discrete output sensors either produce a high level signal or a low level signal.
- The most popular use for these sensors is to determine if an object is present or not.
- They are simple and inexpensive, making them a popular choice for many laser sensor applications.
Discrete output sensors are commonly used in applications such as:
- Conveyor lines
- Level control
- Security systems
Analog output sensors
- A signal from analog output sensors is proportionate to the object's distance from the sensor.
- Compared to discrete output sensors, these sensors are more accurate at measuring distance.
- Applications where you need to know the precise distance to an object are where they are used.
Analog output sensors are commonly used in applications such as:
- Laser sensor for distance measurement
- Robotics
- Automation systems
Distance sensors

- To determine how far away something is, one can utilize distance sensors.
- They can function according to several different theories, including as phase measurement, time-of-flight, and triangulation.
- Numerous industries, such as robotics, automation, and manufacturing, use distance sensors.
Distance sensors are commonly used in applications such as:
- Quality control
- Dimensional measurement
- Robot navigation
Position sensors
- To find an object's position, position sensors are utilized.
- Linear or angular position can be measured by them.
- Applications for position sensors are numerous and include medical devices, robots, and CNC machine tools.
Position sensors are commonly used in applications such as:
- Part placement
- Motion tracking
- Alignment
Speed sensors

- An object's speed can be determined via speed sensors.
- They are able to gauge angular or linear velocity.
- Sports equipment, speed control systems, and conveyor lines are just a few of the many uses for speed sensors.
Speed sensors are commonly used in applications such as:
- Speed control
- Productivity measurement
- Motion analysis
Each type has its unique advantages and laser sensor applications, making sensors indispensable tools in industrial automation and various other fields.
How to choose the right laser distance sensor
Choosing the right laser distance sensor for your application can seem like a daunting task, as there are many factors to consider.
To help you with this process, I've divided the process into several steps:
1. Determine your needs
- Measurement range: How far do you want to measure? A few millimeters to hundreds of meters are the measurement range of laser distance sensors.
- Accuracy: What kind of measurement accuracy do you need? Laser distance sensors can provide accuracy down to a few millimeters.
- Response speed: What kind of response speed do you need? Some laser distance sensors can take measurements as fast as 1 kHz.
- Interface: What interface do you need? Several interfaces, including digital, Ethernet, and analog, are available for laser distance sensors.
- Size and shape: Do you have any restrictions on the size and shape of the sensor?
- Operating temperature: What temperature range will the sensor operate in?
- Environmental resistance: Do you need a sensor that is resistant to dust, dirt, water, chemicals, or other environmental factors?
2. Select the type of sensor
There are two main types of laser distance sensors:
- Analog sensors: An analog signal proportional to the object's distance is output by these sensors.
- Digital sensors: These sensors output a digital signal that represents the distance to the object.
3. Choose a manufacturer
There are many manufacturers of laser distance sensors, so it is important to choose a reputable manufacturer with a good reputation. Some of the most well-known manufacturers include:
4. Consider additional features
Some laser distance sensors have additional features such as:
- Laser scan points: These sensors can generate multiple distance data points, allowing you to create a profile of an object.
- Integrated illumination: These sensors have built-in lighting that can be used to illuminate an object in low light conditions.
- Multi-object detection: These sensors can detect and measure the distance to multiple objects simultaneously.
5. Compare prices
Prices for laser distance sensors can vary greatly depending on the manufacturer, model, and features. Compare prices from multiple vendors before you make a purchase.
6. Get advice
If you are not sure which laser distance sensor is right for you, please contact your a sales specialist or a trusted Eltra Trade distributor.
Remember:
- Prior to utilizing the laser distance sensor, make sure you have read the operating instructions.
- When using the laser distance sensor, according to the safety guidelines.
- To guarantee precise readings, calibrate the laser distance sensor on a regular basis.
- It is possible to select the ideal laser distance sensor for your application by paying attention to these pointers.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and maintenance of laser distance sensors are crucial for ensuring their accuracy, longevity, and reliable performance. Here are some essential tips to help you set up and maintain your sensors effectively.
1. Correct setup for accuracy
Installation:
- Mount the sensor on a flat, stable surface.
- Make sure that the field of view of the sensor is not blocked by any objects.
- Adjust the position of the sensor so that it is pointed at the object you want to measure.
Calibration:
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions for calibrating the sensor.
- Use a calibrated standard if possible.
- Calibrate the sensor regularly to ensure accurate measurements.
Customization:
- Some sensors allow you to customize parameters such as measurement range, resolution, and response time.
- Adjust these settings to suit your needs.
2. Practice regular maintenance
Cleaning:
- Clean the transducer lens regularly with a soft, lint-free cloth.
- Do not use solvents or abrasive materials to clean the lens.
Verification:
- Check the accuracy of the transducer regularly with a calibrated reference.
- If you notice any deviation in accuracy, adjust or replace the transducer.
Maintenance:
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions for servicing the transducer.
- Replace any damaged components.
3. Eliminate common problems
Inaccurate measurements:
- Check that the sensor is properly configured.
- Check that the sensor is calibrated.
- Make sure that the field of view of the sensor is not blocked by any objects.
Signal loss:
- Check the cable connection of the detector.
- Make sure the detector power supply is working properly.
- Check if the detector is damaged.
Signal noise:
- Make sure the detector is not exposed to electromagnetic interference.
- Ground the detector, if possible.
- Use a signal filter if necessary.
You can guarantee correct laser distance sensor installation, upkeep, and operation by adhering to these guidelines.
Conclusion
Industrial automation requires laser distance sensors because of their precision, durability, and adaptability. For best results, installation and maintenance must be done correctly to ensure precise measurements and long-term endurance. These sensors improve productivity, safety, and efficiency in a wide range of applications, including robotics, manufacturing, and the automotive sector. Businesses can use laser sensors to achieve better outcomes by learning about the many kinds of laser sensors, how they operate, and how to maintain them. Laser distance sensors will become more and more important in improving industrial processes and innovation as they continue to advance.