Omron photoelectric sensor
12.07.2024
Omron Corporation, founded in 1933 by Kazuma Tateisi, has become a global leader in industrial automation, renowned for its innovation and reliability. Headquartered in Kyoto, Japan, Omron operates in over 120 countries, providing cutting-edge automation solutions. The company's extensive product portfolio includes sensors, controllers, robotics, and safety systems, all engineered for precision and durability. Omron's photoelectric sensors, in particular, are celebrated for their high performance in diverse industrial applications. The company invests significantly in research and development, dedicating around 7% of its annual revenue to innovation, ensuring it stays ahead in technology. Omron’s commitment to quality is matched by its dedication to sustainability, with initiatives aimed at reducing environmental impact. Through a combination of global reach and local support, Omron delivers exceptional customer service, reinforcing its position as a cornerstone of the industrial automation industry.
What are Photoelectric Sensors?

Advanced gadgets called photoelectric sensors use light to identify objects, surface alterations, and other elements. They are made up of a receiver and a light emitter, or transmitter. In industrial applications such as object counting, location detection, and quality control, these sensors are indispensable. Compared to mechanical switches, their non-contact detecting mechanism reduces wear and tear and increases durability. Photoelectric sensors are widely recognized for their remarkable precision and dependability, especially in demanding industrial settings.
How Omron photoelectric sensors work
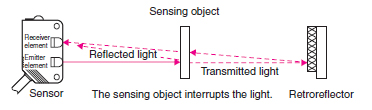
Electronic devices called Omron photoelectric sensors are utilized to determine whether or not things are present. By sending and receiving light, they function.
Main components
- Light emitting diode (LED): Emits a light signal.
- Receiver: Detects the light signal.
- Housing: Protects internal components and provides sensor mounting.
- Electronics: Processes the signal from the receiver and turns off the output signal.
Working principle
- The LED emits a light signal.
- The light signal can be:
- Interrupted by an object: In this case, the signal does not reach the receiver.
- Reflected from a reflector or object: In this case, the signal reaches the receiver.
- The receiver detects the light signal.
- Electronics processes the signal and turns off the output signal.
- The output signal can be used to activate another device, such as a relay or PLC.
Main characteristics of Omron photoelectric sensors
Photoelectric sensors made by Omron are characterized by a wide range of characteristics, which makes them suitable for various applications. Here are some of the most important:
Detection type
- Direct beam: These sensors detect objects crossing the light beam between the emitter and the receiver. They have a wide detection range and are suitable for detecting small details.
- With reflector: These sensors detect objects that reflect the light signal from the reflector. They have a shorter detection range than direct beam sensors, but are insensitive to background illumination.
- Diffuse: These sensors detect objects in the field of light emitted by the LED. They have a short detection range, but are suitable for detecting uneven or non-standard objects.
- Retroreflective: These sensors are similar to sensors with a reflector, but instead of a reflector, they use a special retroreflective film. They have a large detection range and are insensitive to background lighting.
Body size
There are numerous varieties of omron photo sensor available of housing sizes, from miniature to industrial. The choice of case size depends on the space available for installation, and the detection distance required for the application.
Supply voltage
- Most of Omron's photoelectric sensors operate on either 12V or 24V DC.
- Some models are also available with AC power.
Output type
Omron photoelectric sensors have different types of outputs including:
- NPN: This type of output uses an NPN transistor that closes to ground when an object is detected.
- PNP: This type of output uses a PNP transistor that supplies a voltage when an object is detected.
- NO/NC: This type of output has two outputs: normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC). NO closes to NC when an object is detected.
- RS-232: This type of output is used to transmit data from the sensor to a computer or other device.
Detection range
The distance at which an object can be detected by a photoelectric sensor is known as its detection range. The detection range of the sensor depends on its type and body size and power of the LED emitter.
Degree of protection
Omron photoelectric sensors have different degrees of protection (IP) that indicate them resistance to dust and water. The most common degrees of protection for omron photoelectric sensors:
- IP65: Protected against dust and water splashes.
- IP67: Protected against dust and immersion in water up to 1 meter.
- IP68: Shielded from dust and from constant submersion in water.

Additional characteristics
- Size detection function: This function allows the sensor to detect objects of a certain size.
- Shape detection function: This function allows the sensor to detect objects of a certain shape.
- Position detection function: This function allows the sensor to determine the position of the object.
- Communication function: This function allows the sensor to communicate with other devices such as PLCs or computers.
Types of Omron Photoelectric Sensors
A wide variety of photoelectric sensors are available from Omron, tailored to suit different industrial applications. These sensors are categorized into several types:
- Through-beam Sensors: These are perfect for long-range detection because they have a separate transmitter and receiver. By identifying things that block the light beam, they offer the maximum reliability.
- Retro-reflective Sensors: To return the light emitted to the receiver, these devices employ a reflector. Compared to through-beam sensors, they are simpler to install and very useful for detecting translucent objects.
- Diffuse-reflective Sensors: These sensors detect objects by reflecting light off the object's surface back to the receiver. They are suitable for applications where the object's distance varies.
- Distance-settable Sensors: These sensors allow precise adjustment of the detection distance, making them perfect for applications requiring exact distance measurements.
- Fiber-optic Sensors: Flexible and capable of operating in tight spaces or harsh environments, these sensors are ideal for detecting small or hard-to-reach objects.
Each type of Omron photoelectric sensor is engineered for precision, reliability, and durability, ensuring optimal performance in a wide range of industrial applications.
Using Omron Photoelectric Sensors
Omron photoelectric sensors are versatile and reliable devices used in a wide range of applications. They offer many advantages.
Advantages of using Omron photoelectric sensors
- Non-contact detection: Photoelectric sensors are perfect for usage in delicate or dangerous conditions because they don't need to come into direct touch with the object.
- Fast response: Omron photoelectric sensors are perfect for dynamic applications because of their lightning-fast object detection.
- High precision: Sensors can detect objects with high precision, making them ideal for precise measurements.
- Ease of installation: Photoelectric sensors are easy to install and configure, making them ideal for a wide range of users.
- Wide range of applications: omron photo sensor can be used in a wide range of applications such as conveyor lines, packaging machines, door systems and many more.
- Long service life: omron photo electric sensor have a long service life, making them cost-effective.
- Reliability: Photoelectric sensors made by Omron are reliable and resistant to adverse environmental conditions.
- Energy efficiency: Photoelectric sensors consume little energy, making them environmentally friendly.
- Compliance with standards: omron photo electric sensor made by Omron meet international quality and safety standards.
Disadvantages of using Omron photoelectric sensors
- May be sensitive to ambient light: Some types of sensors may misfire in strong sunlight or other bright light.
- May have limited detection range: The detection range of the sensor may be limited by the size and power of the LED emitter.
- Can be sensitive to dirt and dust: Dirt and dust can accumulate on the sensor lens, which can cause false positives.
- Can be expensive: Some models of photoelectric sensors can be expensive compared to competitors.
- May be difficult to program: Some models of Omron photoelectric sensors may be difficult to program for some users.
It is important to note that the advantages and disadvantages of omron photoelectric depend on the specific model of the sensor and on the application for which it is used.

Tips for installing sensor photoelectric omron
Location of the sensor
- Choose a clean and dry location: The sensor should not be exposed to dirt, dust, water or other contaminants that may cause false positives.
- Ensure free access to the sensor: Ensure that the sensor is easily accessible for maintenance and repair.
- Avoid direct sunlight: Some sensor models may malfunction in strong sunlight.
- Consider the distance to the object: The detection range of the sensor depends on its model and size. Make sure that the sensor is installed at a sufficient distance from the object that it will detect.
- Avoid obstructions: Avoid placing the sensor near obstructions that may block the light beam or reflect the signal.
- Consider the direction of movement of the object: Ensure the sensor is positioned such that it can identify objects in the intended direction.
Wiring and connection
- Use the appropriate cable: Use the cable recommended by the manufacturer for the specific sensor model.
- Ensure proper connection: Carefully follow the connection instructions supplied with the sensor.
- Protect the cable from damage: Make sure the cable is protected from sharp edges, overheating, and other potential hazards.
- Grounding: Some sensor models require grounding. Make sure the sensor is properly grounded according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Connecting to a power source: Connect the sensor to an appropriate power source recommended by the manufacturer.
Calibration and testing
- Calibration: Some sensor models require calibration after installation. Make sure you calibrate the sensor according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Testing: After installing and calibrating the sensor, it is important to test it to make sure it is working properly. Use a test object to verify that the sensor detects an object at the correct distance.
- Troubleshooting: If the sensor is not working properly, refer to the operating instructions or an authorized Omron distributor for troubleshooting assistance.
How to Choose the Right sensor photoelectric omron
To guarantee optimum performance for your particular application, carefully evaluate a number of factors when choosing the appropriate Omron photoelectric sensor. Here are the key factors to evaluate:
- Application Requirements: Identify the primary function, such as object detection, counting, or positioning.
- Detection Distance: Determine the necessary range for detecting objects, whether it’s short or long distance.
- Object Characteristics: Consider the size, shape, and material of the object, as these influence sensor selection.
- Sensor Type: Choose between through-beam, retro-reflective, diffuse-reflective, distance-settable, or fiber-optic sensors based on application needs.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess factors like dust, moisture, temperature, and ambient light to select a sensor capable of operating effectively in those conditions.
- Response Time: Ensure the sensor's response time meets the speed requirements of your application.
- Sensitivity and Accuracy: Look for sensors with the appropriate sensitivity and accuracy to achieve reliable detection.
- Output Type: Choose the correct output type (e.g., NPN, PNP, analog) compatible with your control system.
- Mounting and Space Constraints: Consider the physical dimensions and mounting options to fit the available space.
- Power Supply: Ensure the sensor’s voltage requirements are compatible with your system.
By thoroughly evaluating these parameters, you can select the most suitable Omron photoelectric sensor to enhance the efficiency and reliability of your industrial automation processes.
Conclusion
Omron photoelectric sensors are essential for enhancing industrial automation processes due to their precision, reliability, and versatility. These sensors offer high accuracy in detecting objects, robust performance in harsh environments, and non-contact operation that minimizes wear and tear. By integrating Omron sensors, industries can achieve improved productivity, efficient quality control, and streamlined operations. Omron's commitment to innovation ensures that their sensors continue to evolve, meeting the complex demands of modern manufacturing and automation. Embracing omron photoelectric sensor equips industries with the tools needed to optimize efficiency and maintain high standards of performance in diverse industrial applications.
Eltra Trade offers a diverse selection of Omron sensor photoelectric, encompassing through-beam, retro-reflective, diffuse-reflective, distance-settable, and fiber-optic variants. Our knowledgeable managers are always on hand to assist in choosing the right sensor and addressing any inquiries. We provide worldwide delivery and strive to offer the most competitive prices, ensuring our customers receive exceptional value and service for their industrial automation needs.