Pneumatic Foot Valves: A Strategic Approach to Precision Control in Automation
14.03.2024
In this exploration of pneumatic foot valves, we examine their essential function within the realm of industrial automation. These seemingly simple devices play a crucial role in coordinating the precise movements of pneumatic systems. As we dissect their intricacies, from mechanical design to ergonomic functionality, we reveal the often-overlooked contributors to seamless control.
Definition and Purpose Pneumatic foot valve
The pneumatic foot valve is an important element in industrial automation systems. It is used to control the flow of various working media such as air, gas, water or other liquids. The main purpose of the foot operated pneumatic control valves is to quickly and effectively shut off or regulate the flow of the working medium with the help of a foot pedal, which allows the operator to free his hands for other tasks. This is of great importance for the safety and efficiency of work processes, especially in conditions where the speed of reaction is critical.
Significance in Industrial Automation
Pneumatic foot valves are not just convenient devices that free the operator's hands. Their role in industrial automation is much broader and deeper, because they make a significant contribution to:
1. Efficiency
- Automate routine tasks: Instead of manually operating valves by hand, pneuma valves automate the process, saving time and resources.
- Increased Productivity: Fast and precise airflow control provided by foot valves allows operators to get work done faster, increasing overall productivity.
- Reducing the risk of errors: Automation with foot valves minimizes the human factor, reducing the risk of errors that can lead to defects or accidents.

2. Security
- Reduced risk of injury: Foot valves allow operators to safely control pneumatic systems from a distance without risking injury from moving parts or compressed air.
- Ergonomics: Thanks to foot control, operators do not overstrain their hands and back, which makes work more ergonomic and reduces the risk of occupational diseases.
- Ability to work in hazardous conditions: Foot valves allow you to control pneumatic systems from a safe distance, making them indispensable in dangerous or hard-to-reach places.
3. Productivity
- Fast and precise control: pneumatic foot operated pedal valve provide instant response to operator actions, allowing precise and fast control of air flow.
- High pressure capability: they are generally designed for high pressure operation, making them indispensable in powerful pneumatic systems.
- Flexibility: the variety of types and models of foot valves makes it possible to choose the best option for any task, providing flexibility and versatility in work.
4. Reliability
- Durability: made of high-quality materials that are resistant to wear and corrosion, which guarantees their long service life.
- Ease of maintenance: simple design, which makes their maintenance easy and affordable.
- Resistance to adverse conditions: most foot valves are resistant to vibration, temperature changes, dust and moisture, which makes them reliable in any operating conditions.
Valve Components
The effectiveness and reliability of pneumatic foot pedal control valve lie in their intricate design, comprising several essential components meticulously engineered to withstand the rigors of industrial environments. Understanding these valve components is paramount for comprehending the inner workings of this vital element in industrial automation.
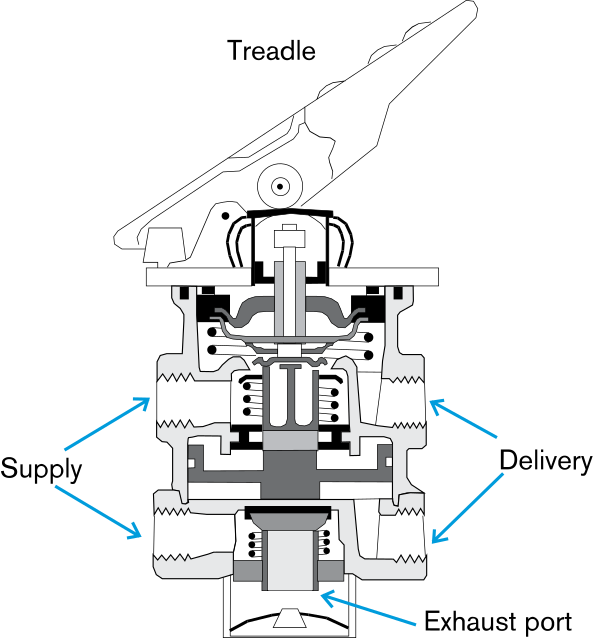
1. Housing
The housing serves as the robust outer shell encapsulating the internal components of the pneumatic foot valve. Engineered from durable materials such as stainless steel or reinforced polymers, the housing provides protection against environmental factors, mechanical stress, and corrosive agents. Its design ensures longevity, resilience, and optimal performance even in challenging industrial conditions.
2. Valve Mechanism
At the heart of the pneumatic foot valve lies the valve mechanism, a precision-engineered assembly responsible for regulating the flow of compressed air. Typically, this mechanism involves a combination of seals, springs, and a valve element. The seals prevent air leakage, the springs provide the necessary force for actuation, and the valve element controls the airflow based on the operator's foot movement. The selection and arrangement of these components are critical to achieving precise control and responsiveness in pneumatic systems.
3. Foot Pedal
The foot pedal represents the interface between the operator and the pneumatic foot valve, translating human input into mechanical action. Constructed for ergonomic comfort and durability, the foot pedal is designed to withstand frequent operation while ensuring a responsive and tactile feel. Operators can exert controlled pressure on the foot pedal, activating the valve mechanism and modulating the airflow with remarkable precision. The engineering of the foot pedal is a key factor in achieving user-friendly and efficient control.
4. Actuation Mechanism
The actuation mechanism is the intricate linkage between the foot pedal and the valve mechanism. Leveraging mechanical linkages or pneumatic actuators, the actuation mechanism ensures a direct and reliable connection, allowing for swift and accurate adjustments to the pneumatic system's parameters.
5. Control Features
Many pneumatic foot valves incorporate additional control features to enhance functionality. This may include adjustable pressure settings, locking mechanisms for continuous operation, or even electronic components for integration into advanced control systems. The careful engineering of these features expands the versatility of foot pedal pneumatic valve, making them adaptable to a wide range of industrial applications.
6. Connectivity Interfaces
To integrate seamlessly within pneumatic systems, pneumatic foot valves are equipped with connectivity interfaces. These interfaces facilitate easy integration into existing systems and provide compatibility with various pneumatic fittings and hoses. The design of these interfaces ensures airtight connections, preventing leakage and optimizing the efficiency of the overall pneumatic system.
Choosing the Right Pneumatic Foot Valve
Selecting the appropriate pneumatic foot valve is a critical decision in the realm of industrial automation, influencing the efficiency, precision, and safety of pneumatic systems.
1. Factors to Consider
- Application Requirements: Before choosing a pneumatic foot valve, it is imperative to define the specific requirements of the application. Consider the nature of the tasks involved, the desired level of control precision, and the environmental conditions. Different applications may demand varying degrees of sensitivity, response time, and resilience, and tailoring the selection to these needs ensures optimal performance.
- Pressure and Flow Requirements:Pneumatic pedal valve come in a range of pressure ratings, and selecting one that aligns with the system's requirements prevents inefficiencies, pressure drops, or potential damage. Likewise, considering the required airflow capacity ensures that the chosen valve can handle the demands of the application without compromise.
- Environment and Durability: Harsh conditions, exposure to contaminants, or extreme temperatures necessitate valves with robust housing materials and sealed components.
- Ergonomics and Operator Comfort: A well-designed foot pedal enhances user comfort, reduces fatigue, and contributes to overall operational efficiency. Prioritizing ergonomics aligns with the goal of creating a user-friendly and safe working environment.
- Maintenance Requirements: Opting for pneumatic foot valves with accessible components, easy disassembly, and straightforward maintenance procedures simplifies upkeep and minimizes downtime. This proactive approach to maintenance contributes to the longevity and reliability of the overall pneumatic system.
2. Compatibility with Systems
- Pneumatic System Design:The chosen pneumatic foot valve should seamlessly integrate into the existing pneumatic system. This involves assessing the compatibility of fittings, hoses, and connectors. The valve's connectivity interfaces must align with the system's specifications to ensure airtight connections, preventing leaks and optimizing overall system efficiency.
- Control System Integration:In scenarios where advanced control systems are in use, compatibility with electronic interfaces becomes crucial. Pneumatic foot valves equipped with electronic control features should integrate seamlessly into the broader automation infrastructure.
- Safety Standards Compliance:Ensure that the chosen pneumatic foot valve complies with relevant safety standards and regulations.
- Scalability and Future Adaptability:Opt for valves that offer scalability and adaptability, allowing for easy integration of additional components or modifications to meet evolving industrial needs.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Pneumatic Foot Valves
Efficient installation and proactive maintenance are crucial aspects of maximizing the functionality and lifespan of pneumatic foot valves in industrial automation.
1. Step-by-Step Guide for Installation
- Assess System Compatibility: Before installation, ensure that the chosen pneumatic foot valve is compatible with the existing pneumatic system. Verify fittings, hoses, and connectors to guarantee seamless integration.
- Locate Optimal Position: Identify the optimal position for installing the foot valve. Consider ergonomic factors, operator convenience, and the proximity to the pneumatic equipment it controls.
- Mounting the Valve: Securely mount the pneumatic foot valve in the chosen position. Use appropriate fasteners to ensure stability. Confirm that the foot pedal is positioned for ease of operation and that the valve mechanism aligns with the direction of airflow.
- Connect Pneumatic Lines: Connect the pneumatic foot valve to the existing pneumatic lines using compatible fittings. Pay close attention to ensure airtight connections, minimizing the risk of leaks.
- Test the System: Conduct thorough testing of the pneumatic system after installation. Verify the responsiveness of the foot valve, check for any unusual noises, and confirm that the airflow meets the specified requirements.
- Implement Safety Measures: Integrate safety measures, such as emergency shut-off procedures, if applicable. Ensure that operators are adequately trained on the proper use of the foot valve and that safety protocols are clearly communicated.
2. Common Maintenance Issues
- Air Leakage: Regularly inspect seals, gaskets, and pneumatic connections for signs of wear or damage.
- Foot Pedal Malfunctions: Clean and lubricate the pedal mechanism regularly. Address any mechanical obstructions promptly to ensure smooth and reliable operation.
- Contaminant Buildup: Regularly inspect and clean the valve mechanism to prevent contaminant buildup, which can impair the valve's functionality and responsiveness.
- Wear and Tear: Implement a proactive maintenance schedule that includes inspections for signs of wear, such as worn-out seals or springs. Replace components as needed to prevent unexpected failures.
- Calibration Issues: Regularly calibrate the valve mechanism to ensure accurate control of airflow. Follow manufacturer guidelines for calibration procedures.
- Environmental Factors: Choose appropriate housing materials and implement protective measures to mitigate the effects of the environment on the valve's durability.
Industry Standards and Regulations
Foot operated pneumatic valve comply with a number of industry standards and regulations. These standards ensure that valves are safe, reliable and meet certain performance characteristics.
The most common standards for pneumatic foot valves:
- ISO 5599-1: Pneumatic devices. Valves. Part 1: General technical conditions.
- DIN 24340: Pneumatic valves. General technical conditions.
- NFPA 70: National Electrical Code (NEC).
- ANSI/NFPA 70E: Standard for Safe Work with Electrical Installations.
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.217: Safety standards for pneumatic and hydraulic systems.
It is important to ensure that the pneumatic foot valve you choose meets all relevant standards and regulations.

Recommended practices:
- Choose valves with CE marking: This means that they meet the basic safety and health requirements of the European Union.
- Use valves that meet your specific needs: Not all valves are the same. Make sure the valve you select has the characteristics required for your application.
- Regularly service and repair the valves: This will help ensure their safe and reliable operation.
Additional tips:
- Contact an industrial automation specialist with: It will help you choose and correctly operate pneumatic foot valves.
- Read the valve's operating instructions before using it: This will help you understand how to properly use and maintain the valve.
- Keep records of valve maintenance and repairs: This will help you monitor their status and ensure their safe and reliable operation.
Future Trends in Pneumatic Foot Valve Technology
Pneumatic foot valves are constantly being improved. Some of the key innovations and developments expected in the coming years include.
- Materials: The development of new, stronger and lighter materials, such as composite materials, will allow the creation of valves that are more durable and economical.
- Energy efficiency: The need for more energy-efficient valves is growing. This will lead to the development of new technologies, such as low pressure drop valves, which allow for energy savings.
- Integration of sensors: More and more valves are equipped with sensors that allow monitoring their condition and operation.
- Modularity: Modular valves, which can be easily configured and adapted to specific needs, are growing in popularity.
Integration with intelligent systems
Pneumatic foot valves are increasingly integrated with intelligent systems such as:
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): IIoT allows valves to be networked, enabling remote monitoring and control.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can be used to analyze data collected by valve sensors to predict malfunctions and optimize operations.
- Machine learning systems: Machine learning systems can be used to automatically adjust and adapt valves to changing operating conditions.
Integration of pneumatic foot valves with intelligent systems will allow:
- Increase productivity
- Reduce operating costs
- Increase security
Conclusion
Pneumatic foot valves are versatile and reliable devices used in a wide range of industries. They provide safe and convenient airflow control, making them indispensable for many pneumatic systems.
When choosing a pneumatic foot valve, it is important to consider factors such as valve type, size, material, operating pressure, temperature, function and compatibility with your systems.
Pneumatic foot valves are important components of many pneumatic systems. When properly selected and operated, they can provide years of trouble-free operation.