The Importance of Rotary Actuators in Industrial Automation
27.08.2025
Modern automation systems increasingly rely on precise motion control to improve efficiency, productivity, and reliability. One of the most important components of such systems are devices that provide rotation control – they allow repeating movement cycles to be performed with high precision.
Rotary actuators in industrial automation play an important role in the implementation of automated rotary motion. They provide a compact and reliable solution for a variety of tasks – from simple rotation to synchronous positioning of elements in robotic systems. Without these components, precise and fast transmission of torque on objects with rotary motion is impossible.
What Is a Rotary Actuator?
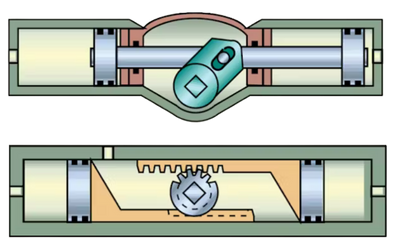
Rotary actuators are drives that convert the energy supply (air, electric, or hydraulic) into controlled rotational motion. Unlike l
inear analogs, which create translational movement, rotary actuator functions provide rotation at a certain angle or with a given number of revolutions. This is especially important when it is necessary to perform angular positioning in automation.
By design, a rotary actuator consists of a drive mechanism, a housing, fasteners, and a torque transmission system. Depending on the technology, gear transmissions, eccentric mechanisms or vane systems can be used.
Types of Rotary Actuators
There are several types of rotary drives, each of which is optimal for certain operating conditions. Different power sources, design features, and precision levels will allow you to choose the right option for almost any task.
Pneumatic Rotary Actuators
Pneumatic actuators use compressed air energy to create a rotating moment. Inside the device there are pistons or vanes, driven by air pressure, which provide rotation of the output shaft. 
Main advantages: simple design, high response speed, reliability in difficult conditions. They are ideal for the automation rotary motion in valve control systems, in simple manipulators and packaging lines.
Pneumatic rotary actuator can also often be used in compact positioning systems where high accuracy is not required, but a high cycle rate is important. These devices are affordable, easy to maintain, and are great for integration into modular pneumatic systems together with guided cylinders.
Electric Rotary Actuators
Electric rotary actuators provide the most precise motion control by using electric motors, gearboxes, and built-in sensors. They are used where high precision and repeatability of operations are required. 
Due to the possibility of programming and easy integration with PLC and other systems, such devices are ideal for motion control automation. Modern models are equipped with encoders, controllers, and digital interfaces, which makes them ideal for use in robotics, assembly lines and quality control systems.
Electric rotary actuators provide stable and predictable behavior even in complex technological processes. They are also easily scalable, which is important when building multi-axis systems.
Hydraulic Rotary Actuators
Hydraulic rotary actuators are solutions designed for high-torque applications. They operate using hydraulic fluid pressure, which is transmitted to internal blades or pistons, thereby creating rotation. 
Their main advantage is the ability to develop significant forces on small dimensions. This makes them indispensable in heavy industry, such as metallurgy, and mechanical engineering, as well as in the control of massive valves or platforms. Industrial rotary actuators of this type require special infrastructure: pumps, tanks, and filters, but at the same time provide stable operation under high load and temperature conditions.
Key Benefits of Rotary Actuators in Automation
Industrial automation systems place high demands on the speed, precision, and reliability of drive mechanisms. In conditions where every second and millimeter is important, rotary actuators are indispensable elements. They can increase production efficiency, reduce costs, and adapt processes to the needs of a specific enterprise. Below, we will present you with the main advantages that explain the widespread use of rotary actuators in industrial automation.
Compact and Efficient Design
One of the most important advantages of rotary drives is their compact and efficient design. Thanks to their minimalist and robust design, such devices can be easily integrated into limited spaces – be it a robot body, a control panel, or a moving conveyor module.
Compactness is especially important when you need to place several mechanisms in a limited space, for example, in assembly modules or laboratory equipment. At the same time, the actuators retain high mechanical strength and load resistance, without losing performance.
In addition, compact rotary systems require fewer fasteners and cables, which simplifies installation and maintenance. This reduces the total cost of ownership of the equipment and speeds up commissioning.
Simplified Angular Positioning
Another advantage is simplified angular positioning. Rotary actuators are designed specifically for precise rotation at a predetermined angle. This can be 90°, 180°, 270°, or even infinite rotation, depending on the configuration.
This simplified angle control makes actuators ideal for repeatable tasks where it is important to achieve high accuracy without complex software solutions. At the same time, they can provide both unidirectional and reversible movement.
Modern models allow you to easily set the rotation angle via the controller or manually, providing flexibility and adaptability in automated processes. This is especially important in systems that require angular positioning in automation without operator intervention.
Integration with Sensors and Controls
Modern rotary actuator applications rarely exist in isolation from the control system. Most models are easily integrated with PLCs, encoders, position sensors, and other elements of industrial electronics.
This integration with sensors and controls allows you to create closed control loops, where the actuator's movement depends on external conditions - the position of the object, pressure, temperature, or a signal from a machine vision camera. Such synchronization increases the safety and efficiency of the entire line.
Electric models are especially well suited for such integration. For example, an electric rotary actuator can receive signals from a controller and perform rotation with an accuracy of fractions of a degree. Feedback is also possible - the device "informs" the system of its current position or status.
Increased Speed and Productivity
Another obvious advantage is increased speed and productivity. Due to the high frequency of responses, minimal response time, and low friction, rotary drives are capable of performing a large number of cycles per unit of time.
Unlike mechanical levers or manual operations, automated rotary motion allows you to perform tens and hundreds of actions per minute without losing quality. This is especially important for packaging, sorting, as well as printing, marking, and other processes where the pace of production plays a decisive role.
Increased productivity directly affects the economic performance of the enterprise: the production time per unit of output is reduced, personnel costs are reduced and the total output of finished products is increased.
Suitable for Repetitive and High-Cycle Tasks
Finally, rotary actuators are ideal for repetitive tasks. Rotary mechanisms are designed for high cycle rates and durability. This makes them ideal for tasks that require tens of thousands of actions per day.
Unlike linear or manual solutions, such systems demonstrate stable operation even under intensive loads. Pneumatic rotary actuators, for example, can operate continuously in assembly lines without overheating or wear due to their simple design and reliable materials.
Typical Industrial Applications
Due to the versatility of the design and the wide range of performance characteristics, rotary actuator uses cover many areas:
- Pick-and-place units in robotics. Rotary actuators are used to position manipulators, especially in pick-and-place systems. Their compactness and high precision make them ideal for robotics;
- Valve actuation in process control. In the chemical, food, and oil and gas industries, pneumatic rotary actuators allow you to open and close shut-off valves remotely;
- Assembly line rotation and indexing. On assembly lines, rotary actuators are used to step-by-step move products between work positions. This allows you to accurately position products without stopping the entire line;
- Material handling and packaging systems. In packaging and sorting lines, rotary actuators ensure synchronous rotation of platforms, separators, and guide mechanisms. They are optimal for transporting products;
- CNC machines and automated tools. In metalworking and engraving machines, such devices are responsible for turning spindles, tools, or workpieces. High precision, compactness, and reliability make them the standard in modern automation.
How to Choose the Right Rotary Actuator
When choosing the right actuator for rotation control, you need to consider some factors:
- Torque. This determines the ability of the device to rotate a given object. For heavy loads, hydraulic actuators may be required;
- The angle of rotation. Some models provide a full revolution, while others provide a strictly limited angle. This is critical for rotary actuator applications;
- Cycle speed and frequency. Pneumatic models are suitable for high-frequency processes, while electric models are suitable for smooth positioning;
- Environment. It is important to consider temperature, humidity, contamination, and IP protection requirements.
When comparing pneumatic vs electric actuators, it is worth considering accuracy, response, and integration with the control system. Electric models are better suited for applications with variable parameters and the need for feedback control.
Also important are the mounting options: flanged, through-hole, with integrated bearings. Feedback is realized through sensors, encoders, or simple signaling devices. All of this is critical when choosing an actuator for rotation control.
Conclusion
Industrial rotary motion remains one of the basic types of motion in modern automation. Types of rotary actuators, including pneumatic, electric, and hydraulic, can solve a wide range of tasks – from precise positioning to controlling massive mechanisms. They provide stability, compactness, and high performance, which makes them indispensable for the automation rotary motion in a wide variety of industries.
Looking for the optimal solution for rotary motion? Explore our range of rotary actuators at ELTRA TRADE and find the perfect fit for your industrial automation needs.