What is Rotary Air Actuator?
17.04.2023
If it is necessary to automate the process of controlling pipeline valves, electric drives are most often used. However, there are technological processes, production facilities, and facilities where their use, even in an explosion-proof version, is undesirable or completely prohibited. Pneumatic actuators are the most common alternative equipment. Today we will take a closer look at what is a rotary actuator, as well as the principle of its operation and its advantages and disadvantages.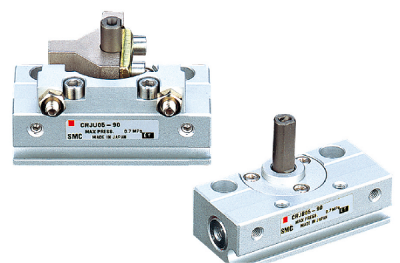
What is a Rotary Air Actuator?
Pneumatic rotary actuators convert pneumatic, hydraulic, or electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Pneumatic rotary actuators use compressed air pressure to create oscillatory rotary motions.
The energy source for the pneumatic actuators is compressed air, which can be supplied from a compressor unit or from a tank. It acts in a certain direction on the movable element, which in turn directly or with the help of a transmission mechanism moves the stem of the locking body. At the same time, depending on the type of actuators, this process can be organized in various ways.
By design, rotary pneumatic actuators are divided into:
- piston;
- bladed.
Depending on the principle of operation, rotary pneumatic actuators are also divided into one-way, in which the main working body moves under the action of air in only one direction (forward or reverse), and returns under the action of a spring or other mechanism, and two-way, in which all actions are provided by pneumatic energy. The movement of the output link can be translational and rotary.
Rotary actuator applications include the following:
- They are used in several motion control systems, as well as to control clamps or manipulators.
- Rotary actuators are often used in the aerospace industry to convert high-speed rotary motion to low torque, etc.
- They are used in agricultural applications to rotate booms, jibs, or other devices in a specific area.
- Hydraulic rotary actuators are commonly used in applications where high torques are required.
- These are used in industries for positioning, transferring & clamping of parts.
- It is a pneumatic cylinder used to create an angular or rotational motion by simply allowing the stroke to oscillate at a certain angle.
- They are used in industry, ships, material handling, robotics, metal processing, etc.
How does a Rotary Air Actuator Work?
Rotary pneumatic actuators - a device that converts the energy of compressed air into a rotary movement of the output shaft of the pneumatic actuators, to transmit torque to a controlled device (buttery valve, ball valve, etc.). As a rule, the rotation angle is limited to the range of 0-90 degrees, however, in some cases, it is necessary to use pneumatic actuators with a rotation angle of up to 180 degrees (for example, to control flow switches or three-way diverting ball valves).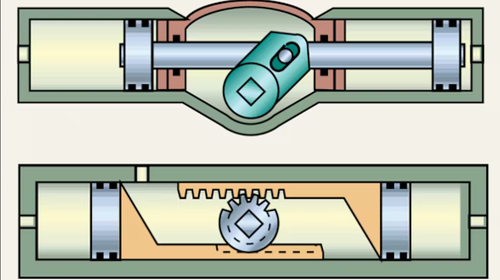
When compressed air is supplied between the body of the rotary pneumatic actuator and the pistons, the latter move and rotate the toothed output shaft using a rack and pinion gear, which engages with the latter. Reverse rotation is carried out either by applying pressure B to the opposite actuator cavity or by means of return springs. Accordingly, the larger the piston diameter, the greater the force it transmits to the output shaft, and the greater the output torque.
A feature of rotary actuators pneumatic is flexible angle configuration rather than fixed values. This means that the movement will be as smooth as possible. The high-quality stainless steel of the case reliably protects accessories. These pneumatic cylinders can operate in various environments, including aggressive ones.
How do I select a rotary actuator?
Rotary actuators are the most compact devices for generating torque from pneumatic or hydraulic pressure. Whether you need a rotary actuator, fast or slow, heavy or light, complex or simple, we have the perfect solution for you.
As part of our extensive range of rotary actuators, we can offer a wide range of rack and pinion rotary actuators and rotary vane actuators to suit a wide range of drive applications.
When choosing a pneumatic rotary actuator for your application, you must weigh mechanical efficiency, size, shaft options, rotational speed, and of course, cost. In addition, it is also useful to consider some broader factors including backlash, the drive's ability to take axial and radial loads on the shaft, and its ability to stop the load.
Rotary actuators with rack and pinion
Rack and pinion rotary actuators are ideal for high-speed manufacturing applications requiring minimal wear and long-life reliability. Offering the widest range of torque and rotation, rotary actuators offer superior mechanical efficiency. Often this figure can reach 90-95%. Rotary actuators are designed for simplified mounting. For example, hollow gears allow the machine shaft to pass through the drive gear, eliminating the need for a clutch.
Among our most popular rack and pinion actuators are compact. Ideally suited for material handling applications, these models include load-bearing bearings and a rack and pinion rotary actuators mounting surface. Available in various sizes, with automatic switching and rotation adjustment from 0 to 190 degrees.
Rotary vane actuators
Rotary vane actuators are ideal for applications where space is limited due to their compact size. Rotary vane actuators, commonly used in medium-speed applications for clamping, moving, or positioning light loads, provide reasonable levels of mechanical efficiency and minimal bypass leakage. Positioning is precise and free of play, and due to their relatively low cost, vane actuators are an excellent choice for light to medium-duty pneumatic applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rotary Air Actuators
The benefits of a rotary actuator include:
- They are durable and provide relatively high torque for their size.
- This reduces maintenance problems.
- These actuators are rotatable so they can easily move different objects at any desired angle.
- This drive is very stable after actuation and even at low speeds.
- It provides very smooth acceleration and braking.
- Rotary drive with stepper motor, speed, and position adjustment is easy.
The disadvantages of rotary actuators include the following:
- The vane drive has limited torque and rotation compared to a rack and pinion drive, typically up to 280° for the single vane model. Thus, they are suitable for light loads in medium-speed applications.
- These drives can only handle light loads because small sleeve-type bearings are used on the shaft.
- Minimum impact power.
- External stops are usually required for high-speed applications.