Inductive Sensors Working Principle
04.12.2022
Various industrial devices involve the use of various sensors, which differ in their features and principles of operation. One of the options that have become quite widespread is an inductive sensor, which is actively used in lower equipment for various systems that provide automated control of production lines.
You can meet such sensors in devices that are responsible for the operation of food and textile industries, engineering enterprises, and many others. Today we will take a closer look at the proximity sensor types and working principle.
What is an Inductive Sensor?
An inductive sensor is a device whose action is based on a changing magnetic field in an inductive coil. When an object made of metal enters its field of action, it is captured and recognized. A circuit built into the device produces electromagnetic radiation. When an induced voltage appears in it, the oscillations decrease. Inductive sensors read this immediately.
Simply put, an inductive sensor is a proximity switch that got its name because of the principle of operation. The sensor has a sensor element with a magnetic circuit open towards the working surface of the sensor.
Like various other devices, these have their pros and cons, which become noticeable in operation. Sensors have become quite popular due to the fact that they have several important advantages.
- The design of these units is quite simple, it does not contain any complex elements that require special settings. Due to this, the sensors are highly durable and reliable, break down infrequently, and can be constantly used in production. It is also convenient that they do not have sliding contacts.
- The features of the device allow you to connect devices to an industrial voltage system without any problems.
- They have good sensitivity, so they can be used when working with various metal objects.
The disadvantages include the fact that during operation, the sensors can produce errors due to the presence of various factors. They can be affected by temperature, as well as exposure to other fields of a similar type. Therefore, for high-quality work, it is necessary to provide suitable conditions that would not prevent the sensors from functioning correctly.
Where Inductive Sensors are Used?
Inductive sensors are known for their reliability and safety in harsh environments. This makes them the best choice for the military, aerospace, railroad, and heavy industries. Inductive sensors are also used in machine tools, machines for the textile industry, the automotive industry, assembly lines, etc. They are used to detect metal parts in difficult environments and where fast moving parts need to be inspected.
An inductive type sensor is designed to control the movement of the working body without direct contact with it. This sensor creates an electromagnetic field in the area of sensitivity and has a semiconductor switch.
The scope of application of inductive sensors is largely determined by their high reliability and resistance to external factors. Many environmental factors do not affect their readings and operation: moisture, condensation, accumulation of dust and dirt, and ingress of solid particles. Such features are provided by their device and design data.
What are the Two Types of Inductive Sensors?
In practice, there is a huge variety of inductive sensors, all of which can be divided into two large categories, depending on the type of supply current - AC and DC. Depending on the state of the contacts, inductive sensors are:

- Closing - when the controlled object is moved, it is switched to the on position.
- Opening - in case of impact, the inductive sensor switches the contacts to the off position.
- Switching - simultaneously combines both previous options, for one switching it puts one output on, the second, in the off position.
According to the number of measuring circuits, inductive sensors are divided into single and differential. The first of them has one coil and one measurement circuit. The second type implies the presence of two sensors, the measuring circuits of which are included in the antiphase to compare readings. A single inductive sensor contains one measuring branch and a differential one-two.
In a differential inductive sensor, when the measured parameter changes, the inductances of two identical coils change simultaneously, and the change occurs by the same amount, but with the opposite sign.
Differential inductive sensors are a combination of two non-reversible sensors and are made in the form of a system consisting of two magnetic circuits with a common armature and two coils. Differential inductive sensors require two separate power supplies.
According to the method of data transmission, inductive sensors are divided into analog, electronic and digital. In the first case, the same coils and ferromagnetic cores are used. Electronic ones use a Schmidt trigger instead of ferromagnets to obtain a hysteresis component. Digital ones are made in the format of printed circuit boards on microcircuits. In addition, the types are divided according to the number of sensors leads two, three, four, or five.
Working Principle of Inductive Sensor
This type of sensor, due to its internal structure, has a certain inductive sensor working principle. It uses a unique generator that produces a certain amplitude of oscillation. When an object consisting of a metallic or ferromagnetic material enters the field of action of the unit, the vibrations begin to change, which indicates the presence of an object. Because of this, the sensors work only with similar materials and are useless in other cases.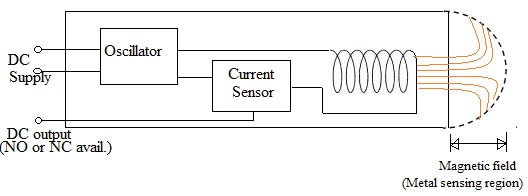
When starting work, the limit switch is energized, which contributes to the formation of a magnetic field. It is it that affects the eddy currents, which, in turn, change the amplitude of the oscillations of a working generator.
The result of all these transformations is an output signal, which can vary depending on the distance between the working sensor and the object under study. Then, using a special device, the analog signal is converted into a logical one.
An inductive sensor is also needed to recognize the position of metal objects. This can play an important role in production. If products follow along the line, on which metal parts must be arranged in a certain order, then the sensors will check the correctness of this arrangement. If an error is detected, the device will signal the conveyor and the software will take further action to correct the problem.
In addition to the response range or sensitivity, the inductive proximity sensor working principle is characterized by the following performance characteristics:
- The size (diameter) of the fitting thread, for various samples, takes values from 8 to 30 mm.
- Rated supply voltage at a temperature of plus 20 degrees, up to 90 Volts DC, and up to 230 Volts AC.
- The overall length of the housing - its value depends on the operating voltage.
- The latter indicator for different samples can vary significantly.
For the sensitive or active zone of the device, another parameter is introduced, called the guaranteed response limit. Its lower limit is zero, and the upper limit is 80 percent of the nominal value. This figure is sometimes referred to as the operating clearance correction factor.
An equally important indicator of the functionality of a sensitive device is the number of connecting wires in the connector. Usually, there are two or three of them: two supply and one to activate the circuit. However, connection options are possible, the arrangement of which uses four or five contact points. Such samples, in addition to two supply conductors, contain two outputs to the load. In this case, the fifth conductor is used to select the operating mode of the device itself.
Applications of Inductive Sensors
A typical application of inductive sensors in industrial automation is similar to the function of limit switches (or limit switches). Such sensors are one of the popular devices used to detect the presence of objects in industrial automation and automated production control systems.
Inductive sensors are triggered when a metal object approaches (it can be geared teeth, cams, a metal part, etc.). Thus, the sensors are not sensitive to interference and work even under harsh industrial conditions.
Also, the inductive sensor works for such industrial niches as:
- Medical devices.
- Appliances.
- Automotive industry.
- Robotic equipment.
- The industrial technology of regulation and measurement.