Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Quick Review of Their Differences
16.05.2025
In modern industrial production, construction, as well as medicine and even in the service sector, fluid power systems are widely used, that is, systems in which energy is transmitted employing liquid or gas. These technologies are the basis for automation, motion control, and various machines and equipment actuation.
The two main categories: hydraulic systems and pneumatic systems. Despite the common essence (using pressure to transmit energy), there are many differences between them that directly affect the choice of equipment, its performance and operating costs.
Understanding the difference between hydraulic and pneumatic systems is vital for engineers, technologists and automation specialists. After all, the reliability, accuracy and efficiency of the entire production process depend on it. To make the right choice and not make a mistake when designing equipment, it is important to consider all the nuances: from pressure to requirements for the cleanliness of the environment, from the availability of components to the project budget. Below we will consider in detail hydraulic and pneumatic systems, their differences, advantages and disadvantages and much more.
CONTENT:
- What Are Hydraulic Systems?
- What Are Pneumatic Systems?
- Key Differences Between Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems
- Pros and Cons of Each System
- Application Areas: Where Each System Works Best
- Conclusion
What Are Hydraulic Systems?
Hydraulic systems use an incompressible liquid (usually mineral oil) under high pressure to operate mechanisms. The pressure is transmitted through pipelines to the actuators, thereby creating a powerful and smooth movement.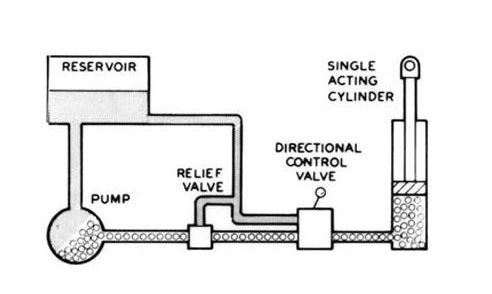
The operating principle of such systems is based on Pascal's law: the pressure that is applied to the liquid in a closed volume is transmitted unchanged in all directions. This allows for the efficient conversion of mechanical energy from the pump into a force that acts on the actuator. In closed-loop systems, the oil circulates in a circle, which ensures stability and repeatability of operation.
The main components of such systems are:
- A pump that creates an oil flow;
- An actuator, such as hydraulic cylinders or hydraulic motors, that converts pressure energy into linear or rotational motion;
- A reservoir for storing liquid;
- Filters, sensors, and control valves that ensure safety, cleanliness, and precision of operation;
- Coolers and safety valves that protect the system from overheating and excess pressure.
Applications include:
- Heavy construction equipment (excavators, bulldozers);
- Hydraulic presses and forging machines;
- Casting and molding machines;
- Aerial platforms and lifts;
- Marine technology and shipbuilding;
- Aerospace and mobile technology.
Thanks to the high density of transmitted energy, hydraulic motion control allows controlling massive and powerful systems with relatively compact dimensions of components. This makes hydraulics indispensable where great force and precise adjustment of movement are required.
In Eltra Trade you can find a full range of components for hydraulic systems: from pumps to filters, from sensors to valves from leading manufacturers.
What Are Pneumatic Systems?
In pneumatic systems, the source of energy is compressed air or another gas. It is pumped into the system by a compressor, and then supplied under pressure to pneumatic cylinders or other actuators. Such systems are less powerful, but are characterized by the speed of reaction, simplicity and environmental friendliness.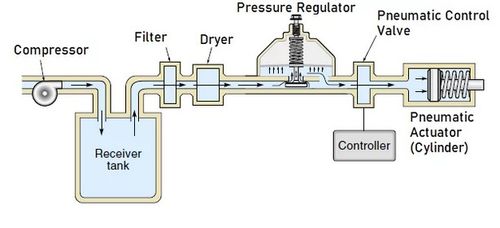
Main components:
- Compressor, which creates an air flow;
- Receiver for pressure accumulation;
- Valves, which regulate the flow and direction;
- Pneumatic cylinders, which perform the movement;
- Filters, dryers and separators, which prevent moisture and particles from entering the system;
- Air preparation systems, such as pressure regulators and lubricators.
Such systems are used in:
- Automated assembly lines;
- Packaging machines and robotic manipulators;
- Food and pharmaceutical industries;
- Laboratories and clean rooms;
- Pneumatic tools and car services;
- Bottling and packaging lines.
One of the main advantages is cleanliness. Since compressed air systems do not contain oil and leave no traces, they are ideal for industrial automation systems with high sanitary requirements. Simple designs and quick setup make pneumatics indispensable in flexible production conditions.
If you need reliable pneumatic components, contact Eltra Trade - we will supply any compressed air products: from filters to cylinders and solenoid valves.
Key Differences Between Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems
To understand the difference between hydraulic and pneumatic systems, let's look at their main parameters:
Feature | Hydraulics | Pneumatics |
Working Medium | Oil (liquid) | Compressed air (gas) |
Pressure Range | High (up to 700 bar) | Low to medium (up to 10 bar) |
Force Output | High | Moderate |
Precision | High | Lower |
Speed Control | Slower but smooth | Faster response time |
Cleanliness | Prone to leakage, not clean | Cleaner, no risk of oil contamination |
Noise | Quieter | Louder (due to air exhaust) |
Cost | Higher installation cost | Lower cost, simpler setup |
Feature | Hydraulics | Pneumatics |
Working Medium | Oil (liquid) | Compressed air (gas) |
This fluid power comparison shows that pneumatic vs hydraulic is not just a choice between two types of actuators. It is a strategic decision that depends on the tasks, conditions and your budget. Evaluating these characteristics will help you choose the most efficient system for your project requirements.
Pros and Cons of Each System
Now let's take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of both types of systems.
Advantages of Hydraulics
- High force output;
- Accurate and smooth motion;
- Compact components for heavy-duty power;
- Durability of components;
- Possibility of multi-stage regulation;
- Wide range of equipment and accessories.
Disadvantages of Hydraulics
- Higher cost;
- Risk of fluid leakage;
- Requires maintenance and filtration;
- Complexity of installation and adjustment;
- High level of maintenance;
Advantages of Pneumatics
- Clean and safe for sensitive environments;
- Fast and lightweight components;
- Lower upfront and operating costs;
- Ease of installation and operation;
- High response speed;
- Possibility of integration into compressed air vs hydraulic oil systems;
- Low level of inertia of moving parts.
Disadvantages of Pneumatics
- Less force and control;
- Requires air drying and filtering;
- Noisy operation without silencers;
- Difficulty in maintaining stable pressure;
- Lower positioning accuracy;
- Limitations on air transportation distance.
In Eltra Trade you can get detailed advice on equipment selection based on the advantages of each system and the specifics of your production.
Application Areas: Where Each System Works Best
Now let's find out in what applications you can use each of the systems.
Where is it better to use hydraulics
- Lifting and heavy construction equipment;

- Metalworking machines;
- Presses and molding systems;
- Injection molding machines and molds;
- Agricultural machines and combines;
- Marine and ship machinery;
- Aerospace equipment;
- Heavy industrial presses and hydraulic manipulators.
Where pneumatics are effective
- Automated assembly lines;
- Food and pharmaceutical production;
- Pneumatic transport systems;
- Robotics and manipulators;
- Packaging and packaging equipment;
- Pneumatic tools and equipment in car services;
- Equipment in clean rooms;
- Textile and light manufacturing.
Thanks to the wide range of products from Eltra Trade, you can be sure that you will receive the most effective solution specifically for your needs.
How to Choose Between Pneumatics and Hydraulics
When choosing between pneumatic vs hydraulic actuators, there are several key factors to consider:
- Required force and pressure. For heavy loads, it is better to choose hydraulics.

- Expected precision and smoothness. If controlled flow is important, hydraulics.
- Cleanliness and safety. In a sterile environment and with minimal risks, pneumatics.
- Project budget. Hydraulics are more expensive, but more powerful. Pneumatics are cheaper, but weaker.
- Maintenance. Complex systems require regular qualified support.
- Response speed. Pneumatics wins in dynamics.
- Operating conditions. At high temperatures, in an aggressive environment, the choice of material and component is important.
Hydraulic vs pneumatic systems should be compared not by individual parameters, but in the context of specific operating conditions. For example, sterility is important in a food factory, and enormous force is important in bridge construction.
If you are not sure what is right for you, Eltra Trade specialists will help you decide. We will provide technical documentation, calculations and recommendations for implementation.
Conclusion
Differences in fluid power technologies affect the entire structure of the production system. Hydraulics and pneumatics are two powerful tools, each with its own tasks and advantages. Hydraulics are best suited for heavy loads, precise control and stability in difficult conditions. Pneumatics are for fast, easy and safe operations, especially where cleanliness is critical.
Understanding the features of hydraulic vs pneumatic actuators allows you to increase efficiency, reduce costs and extend the service life of equipment. Evaluate your case, determine priorities and make an informed choice.
Need help choosing between hydraulics and pneumatics? Contact Eltra Trade – we will select components that are optimal in performance and price. We have pneumatic cylinders, hydraulic pumps, filters, valves and other system elements from leading global brands.