Troubleshooting Solenoid Valve Problems: Solutions and Tips
21.02.2024
Solenoid valves are a very popular solution in many industries. Thanks to these devices, you can easily control the flow of liquids and gases in the system. Like any other equipment, they can break down and it is not always possible to determine valve problem solutions at first glance. Therefore, below we will consider in detail solenoid valve problems and ways to solve them.
Common Problems and Their Causes
Valve performance issues can happen for other reasons, and detecting them in time is very important if you want to save your device. Below we will look at solenoid valve failure symptoms and their possible causes.
Failure to open or close
Incorrect or insufficient voltage can prevent the solenoid from generating enough force to actuate the valve. Also, damaged or disconnected wires can disrupt the electrical connection to the solenoid.
Valve leaks or drips
Wear and tear on the valve seal over time can lead to leaks. Regular maintenance and seal replacement may be necessary.
Valve vibrations or noisy operation
Particles in the fluid can cause vibrations and noise. Ensure the system is properly filtered to prevent contamination. Moreover, high pressure can lead to noisy operation. Verify that the pressure is within the recommended range for the solenoid valve.
Excessive heat generation
High voltage or operating it continuously can cause the solenoid coil to overheat. Ensure that the voltage is within the specified range.
Intermittent operation
Inconsistent power supply or voltage fluctuations can result in intermittent operation. Also, loose connections or a damaged coil can lead to it.
Valve sticking
Dirt or particles in the valve can cause it to stick. Regularly clean the valve and fluid lines.Furthermore, inadequate lubrication of moving parts can contribute to sticking.
No response to the control signal
Check the control signal to ensure it is functioning correctly. Use a multimeter to test for continuity in the control circuit.
Coil burnout
Excessive voltage can lead to coil burnout. Ensure that the voltage supplied to the solenoid is within the specified limits. In addition, rapid and frequent cycling of the solenoid can cause the coil to overheat. Adjust the system parameters to reduce unnecessary cycling.
Solenoid Valve Maintenance Guidelines
Proper maintenance of solenoid valves is essential to ensure their reliable and efficient operation over time. Let’s check tips to avoid fuel solenoid valve problems.
- Carry out regular visual checks for any signs of damage, corrosion, or leaks.
- Periodically clean the valve and its components to remove dirt, debris, and any contaminants that may affect performance.
- Perform leak tests regularly to quickly identify and repair any leaks.
- Check the integrity of the electrical solenoid valve connection and wiring.
- Tighten any loose connections and replace damaged wires or connectors.
- Use appropriate lubricants to ensure smooth operation and prevent sticking.
- Check the voltage supplied to the solenoid valve regularly to ensure that it is within the specified range.
- Monitor the temperature of the electromagnetic coil during operation. Excessive heat may cause the coil to burn out.
- If the solenoid valve is part of a fluid system, check and clean the filters or strainers upstream of the valve to prevent debris from entering and causing problems.
Effective Troubleshooting Techniques
Effective troubleshooting of solenoid valves involves a systematic approach to identify and address issues. Here are some solenoid valve repair tips.
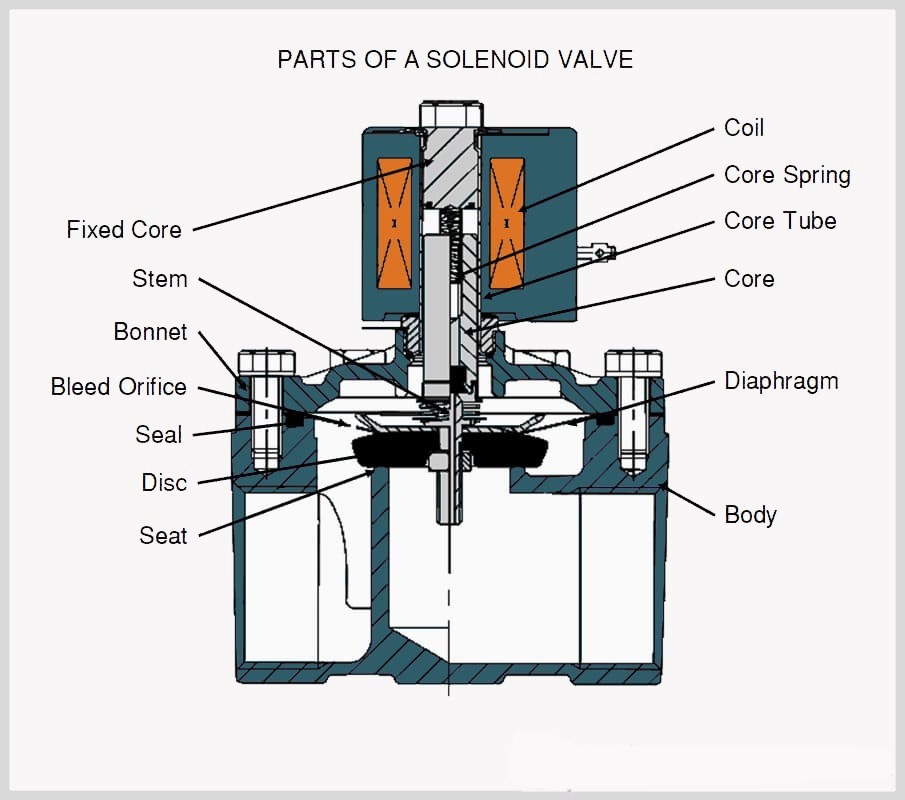
- Become familiar with the entire system in which the solenoid valve is installed, including the control circuit, power source, and fluid lines to know what exact solenoid failure you may face.
- Ensure that the solenoid valve is receiving the correct voltage according to manufacturer specifications.
- Check the control signal (from the controller or PLC) to ensure it reaches the solenoid valve.
- When the solenoid is energized, you should hear a distinctive clicking sound. If not, this may indicate a problem with the coil or the valve itself.
- Inspect the valve for mechanical blockages or obstructions.
- For valves with position indicators, visually verify that the valve is in the expected position during operation.
- Inspect the valve and its connections for signs of leaks.
- Check whether the electromagnetic coil overheats during operation.
- Ensure that system pressure levels are within the recommended range for the solenoid valve.
Preventive Measures for Valve Health
Preventive measures and valve malfunction diagnosis are essential to maintaining the health and longevity of solenoid valves. Implementing these measures can help avoid unexpected failures and downtime. Here are some preventive measures for solenoid valve health.
- Conduct routine visual inspections to check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to prevent any solenoid issue.
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer's recommendations. Perform preventive maintenance tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and component checks at scheduled intervals.
- Install filters or strainers upstream of the solenoid valve to prevent debris and contaminants from entering and causing damage.
- Operate the solenoid valve within the specified pressure and temperature ranges.
- Avoid exceeding the recommended duty cycle to prevent overheating.
- Protect solenoid valves from harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, moisture, and corrosive substances. Install protective covers or enclosures if necessary.
- Ensure a stable and consistent power supply to the solenoid valve. Voltage fluctuations can lead to erratic behavior and damage the coil.
- Train operators and maintenance personnel on proper solenoid valve handling, operation, and maintenance.
- Maintain a comprehensive log of all maintenance activities, inspections, and repairs performed on each solenoid valve.
- Consider upgrading or replacing solenoid valves that are nearing the end of their expected lifespan.
- Establish and communicate emergency shutdown procedures to quickly isolate and address issues with solenoid valves in critical applications.
Choosing the Right Solenoid Valve for Your Needs
Choosing the right solenoid valve for your specific needs requires careful consideration of various factors related to your application. Here are key considerations for you to check.
Fluid compatibility
Ensure that the solenoid valve is compatible with the type of fluid (liquid or gas) it will control. Consider factors such as fluid viscosity, temperature, and chemical compatibility.
Valve type
Select the appropriate valve type based on your application requirements. Common types include:
- 2-way valves: For on/off control.
- 3-way valves: Allow diversion of flow between two ports.
- 4-way valves: Suitable for applications requiring two-position, two-way control.

Valve size and flow rate
Determine the required flow rate for your application and choose a valve size that can handle the specified flow. Consider factors such as pipe diameter, pressure, and required flow characteristics.
Pressure rating
Ensure that the solenoid valve can handle the maximum and minimum pressure levels within your system. Consider both the inlet and outlet pressures.
Voltage and electrical compatibility
Check the available electrical power supply and select a solenoid valve with a voltage rating that matches your system. Verify the compatibility of the valve with your control system (e.g., PLC, relay, or microcontroller).
Environmental conditions
Consider the operating environment, including temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances. Choose a valve with appropriate environmental protection, such as IP (Ingress Protection) ratings.
Duty cycle
Determine the duty cycle of your application, i.e., the percentage of time the solenoid valve will be energized. Select a valve with a duty cycle rating that meets your requirements.
Response time
Evaluate the response time or speed at which the solenoid valve opens and closes. This is crucial for applications requiring rapid changes in flow. Consider the valve's design and construction concerning response time.
Manual override
Some applications may benefit from solenoid valves with manual override features, allowing manual operation during power failures or emergencies.
Certifications and standards
Check for industry-specific certifications and standards compliance. For example, valves used in food or medical applications may need specific certifications.
Budget considerations
Consider your budget constraints while ensuring that the chosen solenoid valve meets all necessary specifications. Evaluate long-term costs, including maintenance and potential downtime.
Installation and maintenance
Consider ease of installation and maintenance requirements. Choose a valve with accessible components and clear documentation for installation and troubleshooting.
Application-specific features
Look for features tailored to your specific application, such as high-temperature seals, corrosion-resistant materials, or special coatings.
Eltra Trade offers a large selection of valves from leading manufacturers such as Eltra, Burkert, Norgren, and others. Our expert managers are available to help with selection and answer any questions. We provide worldwide delivery and competitive pricing, ensuring our customers receive the best.